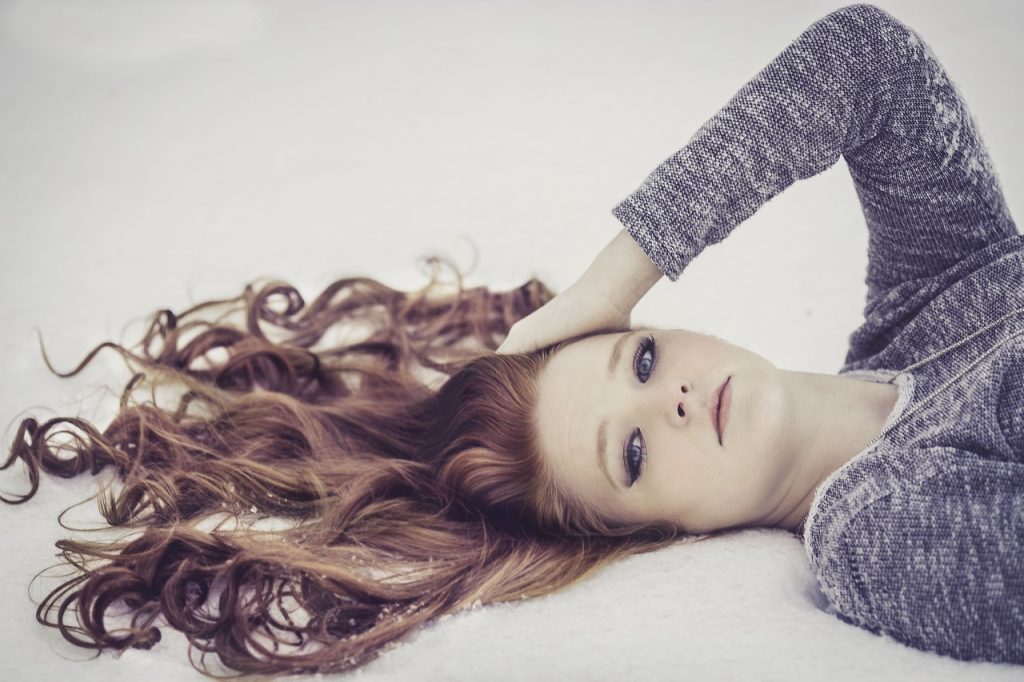
Curly hair, often celebrated for its unique texture and versatility, is a fascinating genetic trait that has intrigued scientists and the general public alike. The diversity in human hair types can be traced back to variations in genes, with curly hair largely attributed to a specific genetic makeup. Understanding whether curly hair is a recessive gene involves delving into the intricacies of human genetics.
The exploration of curly hair genetics has roots in classical studies of heredity that date back to the early 20th century. Researchers initially focused on simple traits that could be easily observed, such as hair texture. It is now understood that hair curliness is influenced by multiple genes, with some indicating that the presence of certain alleles creates the curly phenotype while the absence leads to straighter hair. The significance of this research has grown over the years due to its implications not only in genetics but also in fields like anthropology and personal identity.
A relatable aspect of the curly hair discussion comes from the experiences of individuals navigating hair care routines, often searching for the ultimate products to enhance and define their curls. Compelling statistics suggest that over 60% of people with naturally curly hair feel a deep emotional connection to their hair, reflecting their cultural heritage or personal identity. This connection leads many to explore their genetic background, seeking to understand the hereditary factors behind their unique hair characteristics.
Research has shown that curly hair results from a dominant gene variant, which means it can be passed down through generations, even if only one parent has the trait. Understanding this genetic inheritance becomes crucial not just for those interested in hair but also for those studying human genetics. The intricacies of such traits pave the way for discussions around genetic diversity, making the study of curly hair a significant topic in the broader context of human biological variation.
Through continued research and cultural exploration, the conversation surrounding curly hair remains vibrant and relevant. This fascinating genetic trait not only shapes personal identities but also contributes to the greater narrative of what it means to be diverse in an increasingly interconnected world.
“`html
Is Curly Hair a Result of a Recessive Gene? Discover the Truth Behind Hair Genetics
“`
Curly hair is often thought to stem from genetic inheritance, specifically whether it arises from a recessive gene. In genetics, traits such as hair texture are influenced by multiple genes, with the presence of specific alleles determining whether hair is straight or curly. Generally, the gene responsible for curly hair is indeed considered to be a dominant trait, while straight hair is recessive. This means that individuals with at least one curly hair allele are likely to exhibit curly hair, even if they inherit a straight hair allele from one parent. For a deeper understanding of the genetics behind curly hair and the implications of recessive and dominant traits, continue reading where we delve into the specifics of hair genetics.
Is Curly Hair A Recessive Gene?
The genetics of hair texture, including curly hair, can be quite complex. The common assumption that curly hair is a recessive trait is not entirely accurate. Hair texture is influenced by multiple genes, and the interplay between these genes can produce a wide range of hair types, from straight to wavy and curly.
Genetic Factors Influencing Hair Texture
Hair texture is primarily determined by the shape of the hair follicle, which is genetically inherited. The shape of the follicle can be circular (resulting in straight hair) or oval (resulting in wavy or curly hair). The main genes implicated in hair texture include:
- RSPO2: This gene is involved in hair follicle development and can influence wave patterns in hair.
- WNT10A: Variants of this gene have been associated with hair curliness.
- TRPS1: This gene may also play a role in determining the shape and texture of hair.
Since hair texture is a polygenic trait, multiple genes interact in complex ways, making it difficult to classify curly hair as simply recessive or dominant.
Dominance and Codominance in Hair Texture
In the context of hair texture, it’s essential to understand the concepts of dominance and codominance. Curly hair is often seen as dominant over straight hair, yet the inheritance of hair texture isn’t a straightforward Mendelian trait. Certain combinations can lead to various results such as:
- Curly hair x Straight hair: The offspring may exhibit wavy hair as a result of codominance.
- Curly hair x Wavy hair: This pairing can produce children with a mix of textures, displaying curled and straight characteristics.
Environmental and Epigenetic Factors
Beyond genetics, environmental factors can also impact hair texture. Humidity, for instance, can cause curly hair to appear frizzier, while certain hair products can redefine the way curls look. Furthermore, epigenetic factors, which arise from lifestyle and environmental influences, can modify gene expression without changing the DNA sequence itself, affecting how curly or straight the hair appears.
Genetic Variability Across Populations
Different populations exhibit a diverse range of hair textures due to historical genetic mixing and selective pressures. Populations in tropical regions tend to have curlier hair, possibly as an evolutionary adaptation for heat and humidity, while populations in colder climates may favor straighter hair. This variability shows that while certain genetic traits may be more prevalent in specific groups, there is no singular ‘curly hair gene’ across all human populations.
Conclusion of Genetic Research
Current research into the genetics of hair texture is ongoing, and new discoveries continue to emerge. This complexity reveals that curly hair cannot be strictly labeled as a recessive gene; rather, it is the result of a multitude of genetic interactions, environmental influences, and evolutionary factors that shape how we perceive hair types today.
FAQs about Is Curly Hair A Recessive Gene
What type of inheritance is curly hair?
Curly hair is often associated with genetic traits that exhibit incomplete dominance, meaning that both curly and straight hair attributes can influence the hair type in offspring.
Is curly hair a recessive trait?
While the inheritance of curly hair is complex, it is not purely recessive. Curly hair can be a result of various combinations of genes, which means both curly and straight hair can appear in individuals from the same family.
Can two straight-haired parents have a curly-haired child?
Yes, it is possible. If both parents carry the allele for curly hair (even if they do not express it), they can pass it on to their child, resulting in a curly-haired offspring.
Are there specific genes responsible for curly hair?
Yes, several genes have been identified in relation to hair texture, including the WNT10A gene. Variations in these genes can lead to different hair types, including curly hair.
How do environmental factors affect curly hair?
Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and hair care practices can influence the appearance and health of curly hair, but they do not change the underlying genetic makeup.
Conclusion
The genetic basis of curly hair is complex and cannot be strictly defined as a simple recessive trait. While some studies suggest that curly hair may relate to certain recessive alleles, genetic research indicates that multiple genes are involved, particularly the **KRT17** gene, which influences hair texture. Additionally, the interaction between various genes and environmental factors creates a spectrum of hair types, making it too reductive to label curly hair solely as a recessive trait. This complexity highlights the importance of understanding hair texture through a polygenic lens, where multiple genetic factors contribute to the phenotype.
Furthermore, variations in hair texture persist across different ethnic backgrounds, showcasing the diverse genetic influences at play. The inheritance of curly hair involves both dominant and recessive patterns, depending on an individual’s unique genetic makeup. Ultimately, it is the interplay of multiple genes, epigenetic factors, and environmental influences that dictate whether an individual exhibits curly, wavy, or straight hair. By acknowledging these complexities, we can appreciate the rich tapestry of human genetics that shapes our appearances, moving beyond outdated notions of simple Mendelian inheritance.

Sophia Marie Brown is a haircare and beauty guru with a knack for transforming tresses. With a career that spans salon work and freelance styling, Sophia has a wealth of knowledge on all things hair and beauty. Here on Beautyhill.com She writes about the latest haircare trends, offers advice on maintaining healthy locks, and reviews the best beauty products. Sophia’s passion is to help her readers achieve beautiful, manageable hair that makes them feel confident and fabulous. When she’s not writing, you can find her attending hair expos or experimenting with new hairstyles on her friends.

